Apostila Inglês Instrumental
Transcrição
Apostila Inglês Instrumental
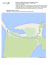
Centro Paula Souza Escola Técnica de Praia Grande Curso Técnico de Farmácia Apostila de Inglês Instrumental Prof.ª Loren Lopes Damásio PRAIA GRANDE 2013 Nome: ...................................................................................... nº........... 3FR..... LESSON 1 PART A Reading Strategies and other facilitators Brainstorm É uma estratégia que consiste na associação de ideias a partir de uma ou mais palavras. Nós a utilizamos, consciente ou inconscientemente, quando tentamos descobrir novos significados através de nosso conhecimento de mundo. Quando lemos um texto, a primeira coisa com que nos deparamos é o título. Um bom título, além de despertar o interesse do leitor, geralmente resume a ideia central do texto. Ao ver um título, podemos começar a fazer previsões sobre o que será tratado no texto, reunindo as informações que já temos sobre o assunto com base em nossa própria experiência. TASK 1 Em português ou inglês, complete o spidergram com palavras relacionadas à INFLUENZA A (H1N1). ETEC de Praia Grande Curso Técnico de Farmácia Inglês Instrumental Prof.ª Loren L. Damásio 1 Nome: ...................................................................................... nº........... 3FR..... 2 Cognatos As palavras de uma língua estrangeira que, além de parecidas na forma, são parecidas também no significado com palavras do português são chamadas de cognatas. A língua inglesa possui várias palavras desse tipo, geralmente derivadas do latim ou do grego. Ao ler um texto em inglês, procure sempre usá-las como apoio. TASK 2 Leia o texto abaixo e destaque as palavras cognatas. 2009 H1N1 2009 H1N1 (sometimes called “swine flu”) is a new influenza virus causing illness in people. This new virus was first detected in people in the United States in April 2009. This virus is spreading from person-to-person worldwide, probably in much the same way that regular seasonal influenza viruses spread. On June 11, 2009, the World Health Organization (WHO) signaled that a pandemic of 2009 H1N1 flu was underway. This virus was originally referred to as “swine flu” because laboratory testing showed that many of the genes in this new virus were very similar to influenza viruses that normally occur in pigs (swine) in North America. But further study has shown that this new virus is very different from what normally circulates in North American pigs. It has two genes from flu viruses that normally circulate in pigs in Europe and Asia and bird (avian) genes and human genes. Scientists call this a "quadruple reassortant" virus. In: http://www.cdc.gov/h1n1flu/qa.htm TASK 3 Com base nas palavras cognatas, responda: 1) Quando o vírus foi detectado pela primeira vez? 2) Como o vírus é propagado? 3) O que a Organização Mundial da Saúde sinalizou? ETEC de Praia Grande Curso Técnico de Farmácia Inglês Instrumental Prof.ª Loren L. Damásio Nome: ...................................................................................... nº........... 3FR..... PART B 3 1. As palavras abaixo de ambas as colunas foram extraídas do texto “2009 H1N1”. Ligue as palavras similares. Para auxiliá-lo(a), baseie-se no texto. (1) Swine (2) H1N1 (3) Referred to (4) Avian (5) People (6) Worldwide (7) North America (8) Influenza (9) In ( ( ( ( ( ( ( ( ( ) United States ) flu ) Person ) On ) Birds ) Called ) Pigs ) Pandemic ) Swine flu 2. Dê um antônimo (oposto) para as palavras abaixo de acordo com o texto: a) old - __________________ b) health - __________________ c) similar - __________________ d) animal - __________________ e) South - __________________ f) separated - __________________ Textos Técnicos Nos textos técnicos escritos em inglês, há grande frequência de palavras de origem grega e latina, as quais, na maioria das vezes, são parecidas com as palavras do português. Quando surge uma palavra especificamente técnica, muitas vezes o próprio texto se encarrega de defini-la. Observe no texto 2009 H1N1 a definição da doença: 2009 H1N1 (sometimes called “swine flu”) is a new influenza virus causing illness in people. ETEC de Praia Grande Curso Técnico de Farmácia Inglês Instrumental Prof.ª Loren L. Damásio Nome: ...................................................................................... nº........... 3FR..... 3. As frases de I a XI são definições de viroses comuns. Considerando-as como respostas, faça perguntas conforme o modelo: A virus is an extremely small organism. It causes disease in humans, animals and plants. What is a virus? I. AIDS is a serious disease. It destroys the body's ability to fight infection. II. Herpes is an infectious disease. It causes painful red spots to appear on the skin, especially on the lips or sexual organs. III. Smallpox is an extremely infectious disease. It causes a fever, spots on the skin and often death. IV. Chickenpox is an infectious disease. It causes a slight fever and red spots on the skin. It is common among children. V. Mumps are an infectious disease. It causes painful swelling in the neck and slight fever. VI. Hepatitis is a serious disease of the liver. There are three main types of hepatitis: hepatitis A, B and C. VII. Measles is an infectious disease. It produces small red spots all over the body. VIII. Cold is a common infection especially in the nose and throat. It often causes a cough, a slight fever and sometimes some pain in the muscles. Flu is like a very bad cold, but it also causes a fever. IX. Polio is a serious infectious disease. Sometimes it causes permanent paralysis. X. German measles or rubella is an infectious disease. It causes red spots on your skin, a cough and a sore throat. XI. Rabies is a fatal disease of the nervous system of dogs and other animals. Sometimes it also causes death in humans who are bitten by an animal with this disease. 4. Complete as palavras-cruzadas com os principais sintomas da gripe dados na figura abaixo. ETEC de Praia Grande Curso Técnico de Farmácia Inglês Instrumental Prof.ª Loren L. Damásio 4 Nome: ...................................................................................... nº........... 3FR..... 5 ETEC de Praia Grande Curso Técnico de Farmácia Inglês Instrumental Prof.ª Loren L. Damásio Nome: ...................................................................................... nº........... 3FR..... 6 5. Após a leitura do mapa, responda as perguntas abaixo: a) Qual a quantidade de mortes no mundo decorrentes de óbitos devido à influenza A (H1N1)? b) Aponte dois países onde houve alto índice de mortalidade devido à pandemia? c) Qual a estimativa de casos de morte por causa da virose no Brasil? d) Aponte cinco países onde houve alto índice de casos da doença? 6. How often do you... a) study? ( ) b) have lab classes? ( ) c) wake up early? ( ) d) go to bed after midnight? ( e) access the internet? ( ) f) play a sport? ( ) g) take pills? ( ) h) go to the doctor? ( ) i) see your dentist? ( ) j) check your weight? ( ) k) get flu? ( ) ) ( 1 ) Always ( 2 ) Frequently ( 3 ) Usually ( 4 ) Sometimes ( 5 ) Hardly ever ( 6 ) Never Pratique com um colega: How often do you study? I always study! 7. Monte frases com as informações do exercício anterior. ETEC de Praia Grande Curso Técnico de Farmácia Inglês Instrumental Prof.ª Loren L. Damásio Nome: ...................................................................................... nº........... 3FR..... 8. Identifque as seguintes partes do SISTEMA RESPIRATÓRIO na figura: right lung, left lung, larynx, pharynx e trachea. ETEC de Praia Grande Curso Técnico de Farmácia Inglês Instrumental Prof.ª Loren L. Damásio 7 Nome: ...................................................................................... nº........... 3FR..... LESSON 2 PART A TASK 1 Dentro da circunferência interna, escreva 3 ou 4 palavras associadas a DIABETES, em português e inglês. Em seguida, compartilhe com seus colegas outras palavras, escrevendo novos itens na circunferência externa. insulin Skimming A palavra skim tem a mesma origem da palavra “escumadeira”, aquele tipo de colher com orifícios pequenos que se passa sobre a superfície de um líquido para retirar resíduos, espuma, nata etc. Essa estratégia, metaforicamente, significa passar uma escumadeira na superfície do texto para retirar o sentido geral (gist). Você faz uma leitura rápida para entender as ideias e conceitos principais. Para tanto, o leitor recorre ao título, subtítulos, ilustrações, nome do autor, a fonte do texto, o início e o final dos parágrafos, itálicos, sumários etc. ETEC de Praia Grande Curso Técnico de Farmácia Inglês Instrumental Prof.ª Loren L. Damásio 8 Nome: ...................................................................................... nº........... 3FR..... TASK 2 Leia o texto a seguir se utilizando da estratégia de leitura skimming. Não se esqueça de, numa segunda leitura, destacar as palavras cognatas do texto. What is diabetes? 1 Diabetes is a disease in which levels of blood glucose, also called blood sugar, are above normal. People with diabetes have problems converting food to energy. 2 Normally, after a meal, the body breaks food down into glucose, which the blood carries to cells throughout the body. 3 Cells use insulin, a hormone made in the pancreas, to help them convert blood glucose into energy. 4 People develop diabetes because the pancreas does not make enough insulin or because the cells in the muscles, liver, and fat do not use insulin properly, or both. 5 As a result, the amount of glucose in the blood increases while the cells are starved of energy. 6 Over the years, high blood glucose, also called hyperglycemia, damages nerves and blood vessels, 7 which can lead to complications such as heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, blindness, nerve problems, gum infections, and amputation. TASK 3 Associe as partes enumeradas do texto às informações que as resumem, dadas a seguir: a) O que acontece com a falta ou mau uso da insulina b) Porque as pessoas desenvolvem diabetes c) Quais danos o excesso de glicose no sangue provoca d) O que é diabetes e) Qual o papel da insulina f) Ao que pode levar os danos do excesso de glicose g) O que acontece com a comida depois da refeição ( ( ( ( ( ( ( ) ) ) ) ) ) ) Scanning É uma estratégia de leitura que significa dar uma lida rápida, folhear um livro, catálogo, manual etc., para achar algo específico como uma data, um nome, um número telefônico, um conceito, uma definição etc. TASK 4 Responda as perguntas a partir do texto, utilizando-se da estratégia de leitura scanning. a) Qual o sinônimo de glicose dado no texto? _________________________________________ b) Qual é o papel da insulina? Em que órgão é produzida? _______________________________ c) Por que as pessoas desenvolvem diabetes? ________________________________________ d) Qual outro nome para diabetes é dado no texto? _____________________________________ e) Quais os principais órgãos do corpo afetados? ______________________________________ ETEC de Praia Grande Curso Técnico de Farmácia Inglês Instrumental Prof.ª Loren L. Damásio 9 Nome: ...................................................................................... nº........... 3FR..... 10 SIMPLE PRESENT TENSE Hyperglycemia damages nerves and blood vessels. Many people have diabetes. Sometimes the pancreas does not make enough insulin. The cells do not use insulin properly. No Presente Simples, basta retirar a partícula TO do infinitivo do verbo e acrescentar: -S na 3ª pessoa do singular; -ES no final de verbos terminados em -SS, -SH, -CH, -X, -Z e -O; -S em verbos terminados em Y precedido de vogal; -ES naqueles terminados em Y antecedido por consoante, trocando, ainda, o Y por I. Na forma negativa, usa-se ainda a partícula de negação NOT junto com o verbo auxiliar DO / DOES que é posicionado antes do verbo principal das frases. TASK 5 Considere as oito palavras em negrito no texto DIABETES. São verbos no tempo presente. Complete a tabela a seguir com trechos do texto, conforme o modelo. SINGULAR SUJEITO AUXILIAR VERBO COMPLEMENTO The body - breaks food down into glucose. PLURAL SUJEITO AUXILIAR ETEC de Praia Grande Curso Técnico de Farmácia VERBO COMPLEMENTO Inglês Instrumental Prof.ª Loren L. Damásio Nome: ...................................................................................... nº........... 3FR..... PART B 11 1. Associe os hormônios às suas definições. A Oestrogene B Progesterone D Adrenaline ( C Testosterone E Insulin ) a hormone in the body which controls the amount of sugar in the blood. ( ) a hormone produced by the body when you are frightened, angry or excited, which makes the heart beat faster and prepares the body to react to danger. ( ) a female hormone that causes development and change in the reproductive organs. ( ) a female hormone which causes the womb to prepare for pregnancy. ( ) a male hormone that causes a stage of growth in older boys and change in their reproductive organs. Contexto O contexto pode ser definido como o encadeamento das ideias de um escrito. Isso significa que, quando lemos um texto em inglês, não devemos considerar as palavras isoladamente, mas dentro de uma frase, que por sua vez faz parte de um parágrafo e assim por diante. 2. Considerando o contexto, complete o texto abaixo com as seguintes palavras: dermatological progestagens medication diabetics oestrogens Hormones and Pharmacology Many hormones and their analogues are used as _______________. The most commonly prescribed hormones are _______________ and _______________ (as methods of hormonal contraception and as HRT), thyroxine (as levothyroxine, for hypothyroidism) and steroids (for autoimmune diseases and several respiratory disorders). Insulin is used by many ________________. Local preparations for use in otolaryngology often contain pharmacologic equivalents of adrenaline, while steroid and vitamin D creams are used extensively in _______________ practice. ETEC de Praia Grande Curso Técnico de Farmácia Inglês Instrumental Prof.ª Loren L. Damásio Nome: ...................................................................................... nº........... 3FR..... 3. Preencha os espaços pontilhados com os respectivos órgãos do sistema digestivo dados no quadro abaixo. esophagus gallbladder mouth small intestine pancreas large intestine rectum liver stomach 4. Complete as palavras-cruzadas com as complicações que a DIABETES pode causar. ETEC de Praia Grande Curso Técnico de Farmácia Inglês Instrumental Prof.ª Loren L. Damásio 12 Nome: ...................................................................................... nº........... 3FR..... LESSON 3 HUMAN BODY FACTS 1. Preencha os espaços das frases abaixo com os verbos dados entre parêntesis. a. The human body ______________ (consist) of a head, neck, torso, two arms and two legs. b. Every square inch of the human body ______________ (have) about 19 million skin cells. c. The average human head ______________ (have) about 100,000 hairs. d. The heart ______________ (beat) more than 2.5 billion times in an average lifetime. e. You ______________ (blink) over 10,000,000 times a year. f. The human brain ______________ (weigh) about 3 pounds. g. It ______________ (take) about 20 seconds for a red blood cell to circulate the entire body. h. Children ______________ (tend) to grow faster in the spring. i. More people ______________ (have) brown eyes than any other color. 2. Identifique as partes do corpo humano nas ilustrações. arm foot hand ETEC de Praia Grande Curso Técnico de Farmácia head leg Inglês Instrumental Prof.ª Loren L. Damásio stomach 13 Nome: ...................................................................................... ear eye mouth nº........... neck 3FR..... nose 3. Complete os espaços em branco com os verbos dados entre parêntesis. a. This system _____________ (consist) of layers of muscles that cover the bones of the skeleton, _____________ (extend) across joints, and _____________ (contract) and _____________ (relax) to produce movement. b. The skeleton is a strong and flexible framework of bones and connective tissue. It _____________ (provide) support for the body and protection for many of its internal parts. c. This system _____________ (consist) of the heart and a network of vessels that carry blood. It _____________ (supply) oxygen and nutrients to the body’s cells and _____________ (remove) waste products. d. This system is the body’s main control system. It _____________ (consist) of the brain, the spinal cord, and a network of nerves extend out to the rest of the body. e. This system is a network of vessels that collect fluid from tissues and return it to the blood. It also _____________ (contain) groups of cells that protect the body against infection. f. This system is centered on the lungs, which work to get life-giving oxygen into the blood. They also _____________ (rid) the body of a waste product, carbon dioxide. g. Hormones _____________ (direct) many body processes, such as growth and energy production. Glands _____________ (release) these chemicals of the endocrine system. h. This system _____________ (take) in the food that the body _____________ (need) to sustain its activities. It _____________ (break) the food down into units called nutrients and absorbs the nutrients into the body. i. The body’s cells _____________ (produce) waste products, many of which urine _____________ (eliminate). Urinary system _____________ (make) urine and _____________ (expel) it from the body. j. The male and female parts of the reproductive system _____________ (produce) the sperm and eggs needed to create a new person. They also _____________ (bring) these tiny cells together. ETEC de Praia Grande Curso Técnico de Farmácia Inglês Instrumental Prof.ª Loren L. Damásio 14 Nome: ...................................................................................... nº........... 3FR..... 3. Associe os dez sistemas do corpo humano dados no quadro abaixo às suas definições, presentes no exercício anterior. Circulatory System ( ) Digestive System ( ) Endocrine System ( ) Excretory System ( ) Lymphatic (Immune) System ( ) Muscular System ( ) Nervous System ( ) Respiratory System ( ) Reproductive System ( ) Skeleton System ( ) 4. Quais sistemas as ilustrações representam? _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ 5. Ao lado dos órgãos abaixo, escreva o nome do sistema do qual fazem parte. a) heart, blood, vessels b) nose, trachea, lungs c) many types of protein, cells, organs, tissues d) bones e) lungs, large intestine, kidneys f) muscles g) glands h) mouth, esophagus, stomach, intestines i) brain, spinal cord, nerves j) male and female reproductive organs ETEC de Praia Grande Curso Técnico de Farmácia Inglês Instrumental Prof.ª Loren L. Damásio 15 Nome: ...................................................................................... nº........... 3FR..... 16 QUESTIONS WITH PRESENT SIMPLE Do you take pills frequently? Do I need to take any medicine? Does your mother work as a pharmacist? Does she work in a compounding pharmacy or in a hospital pharmacy? No Presente Simples, usa-se a seguinte estrutura: Negativa Sujeito + DO (plural) + DOES (singular) Interrogativa DO (plural) DOES (singular) + sujeito Not + + verbo verbo + ? 6. Desembaralhe as frases abaixo, respondendo-as em seguida. a) eight legs? / Does / have /the human body Question: Answer: b) children / Do / in the spring? / grow faster Q: A: c) you/ brown eyes? / have / Do Q: A: d) eggs? / men / produce / Do Q: A: e) many hairs /Do / on their head? / have / people Q: A: f) take long / Does / for a blood cell / the entire body? / to circulate / it Q: A: ETEC de Praia Grande Curso Técnico de Farmácia Inglês Instrumental Prof.ª Loren L. Damásio Nome: ...................................................................................... nº........... 7. Responda as perguntas em inglês, a partir das informações dos exercícios anteriores. a) How many systems does the human body have? b) In general, how many hairs on their heads do people have? c) Why do muscles relax and contract? d) How do cells eliminate waste? e) To which system do the lungs belong? f) What gas do humans inhale, and what gas do they exhale? g) How many livers does the human body have? h) What function does the urine perform? i) What does the body use hormones for? j) Why does the body break food down? k) How long does it take for a blood cell to circulate the entire body? ETEC de Praia Grande Curso Técnico de Farmácia Inglês Instrumental Prof.ª Loren L. Damásio 3FR..... 17 Nome: ...................................................................................... nº........... 3FR..... LESSON 4 PART A 10 MOST PRESCRIBED MEDICINES IN AMERICA Maybe you think America runs on coffee, but it runs on prescription drugs! The billion dollar pharmaceutical industry results in more prescriptions than you can count. Take a look at the 10 most commonly prescribed medicines in America. 1. Lipitor: Lipitor is prescribed to fight high cholesterol in patients. At its peak in 2006, it earned $13.7 billion. 2. Humira: Humira, sold by Abbott Laboratories and Eisai treats rheumatoid arthritis. It is expected to have annual sales of $10.1 billion by 2016. 3. Norvasc: Amlodipine, frequently sold as Norvasc from Pfizer, is a high blood pressure medication with 50.9 million prescriptions. It lost its patent protection in 2007, and generics have become popular. 4. Hydrocodone: The painkiller Hydrocodone with paracetamol was the most widely prescribed individual medication in 2008, with 124 million prescriptions. Hydrocodone and compounds with Hydrocodone are sold under a variety of trademarks, including Vicodin, Hydroccet, Hycodan, and Norco. 5. Amoxicillin: Amoxicillin has been a bestseller for years. It's commonly used by pediatricians for kids, especially ear infections, racking up 49.2 million prescriptions. 6. Zocor: Zocor and its Simivastatin generics are lipid-lowering agents for cholesterol. This prescription drug helped make Merck a high profile drug company. There were 83 million prescriptions in 2009. 7. Lisinopril: This drug has 81.3 million prescriptions. Lisinopril, sold under the brand names Prinivil and Zestril, is in a group of drugs called ACE inhibitors used to treat high blood pressure, congestive heart failure, and improve survival after a heart attack. 8. Synthroid: Millions of Americans do not produce enough thyroid hormone on their own, resulting in 66 million prescriptions of Levothyroxine sodium. It is sold under the names Synthroid, Levoxyl, Levorthroid, and others. 9. Azithromycin: Commonly known as Zithromax, Azithromycin is an antibiotic with 53.8 million prescriptions. It gained popularity because it can be dosed conveniently with little side effects. 10. Metformin: Metformin, also known as Glucophage, Glumetza, Fortamet, and Riomet, is the most important diabetes drug, with 52 million prescriptions. It's trusted as one of the best drugs for lowering blood sugar. Adapted from: <http://www.nursingschools.net/blog/2010/05/10-most-prescribed-medicines-in-america/> Accessed in Aug. 25th 2010 Glossário: Amlodipine: anlodipino, fármaco inibidor do influxo de cálcio, usado para tratar hipertensão e angina. 1. A que a lista de 10 itens do texto acima diz respeito? 2. Que medicamento prescrever-se-ia para as seguintes doenças? a) hipotiroidismo; b) infecção; c) artrite reumatóide; d) diabetes; e) dor de cabeça; f) pressão alta; g) hipercolesterolemia. ETEC de Praia Grande Curso Técnico de Farmácia Inglês Instrumental Prof.ª Loren L. Damásio 18 Nome: ...................................................................................... nº........... 3FR..... 3. De um lado, as classes de medicamento mais comuns; do outro, sua indicação. Associe-as. A. Analgesics B. Antibiotics C. Antiseptics D. Antipyretics ( ( ( ( ) reducing fever (pyrexia/pyresis) ) reducing pain (painkillers) ) inhibiting germ growth ) prevention of germ growth near burns, cuts and wounds DID YOU KNOW… Many of the ingredients for antiseptics come from the rainforests? Some types of antibiotic are used to promote growth in farm animals? PART B Monday, December 28th, 2009 Acute Pharmaceutical Toxicity killed Brittany Murphy by Mike Adams The pharmaceutical industry is based on the idea that for whatever is wrong with you, there is a patented chemical pill that makes it better. Feel some anxiety? There is a pill for that. Have high blood pressure? There is a pill for that, too. Suffer from sleepless nights? There is another pill for that. Importantly, modern medicine and the pharmaceutical industry believe there is no limit to how many prescription medications you can simultaneously take. If you have ten health problems, they have ten different pills for you. And when those pills cause twenty different dangerous side effects, they are ready for twenty more prescriptions for you to dutifully swallow. According to information leaked to the press, Brittany Murphy was found near prescription medications of all the following drugs: • Topamax (anti-seizure medication) • Methylprednisolone (anti-inflammatory drug) • Fluoxetine (antidepressant) • Klonopin (anxiety medication) • Carbamazepine (bipolar medication) • Ativan (anxiety medication) • Vicoprofen (pain reliever) • Propranolol (hypertension drug) • Biaxin (antibiotic) • Hydrocodone (pain medication) Available in: <http://www.naturalnews.com> Accessed in Sep. 8th 2010 1. Destaque no texto as palavras cognatas e as palavras que você já conhecia. 2. O texto “Acute Pharmaceutical Toxicity killed Brittany Murphy” nos permite concluir que: (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) Não há risco de ingerir vários medicamentos simultaneamente. Tomar mais de um medicamento por vez pode ser fatal. Tomar medicamentos sem prescrição médica é muito perigoso. Há medicamento para todos os tipos de doença. Devem-se tomar medicamentos para amenizar os efeitos colaterais de outros medicamentos. ETEC de Praia Grande Curso Técnico de Farmácia Inglês Instrumental Prof.ª Loren L. Damásio 19 Nome: ...................................................................................... nº........... 3FR..... TO BE & THERE TO BE I You He She It We You They Affirmative am are is is is are are are 20 Negative I You He She It We You They am are is is is are are are Interrogative Am I? Are you? Is he? Is she? Is it? Are we? Are you? Are they? not not not not not not not not 3. Destaque no texto as formas do verbo ser, estar e haver. 4. Classifique, de acordo com a tabela, os dez medicamentos possivelmente ingeridos por Brittany Murphy. analgesic antibiotic psychotropic 5. Complete os espaços das frases abaixo com am, is ou are: A) Hellen _______ a doctor, but she _______ unable to practice medicine in her own country. B) "What _______ the dosage?" "One spoonful three times a day." C) ‘Rx’ _______ the abbreviation for ‘prescription’. D) Lisinopril and Zithromax _______ only available on prescription. E) I _______ a pharmacy technician. 6. Leia o modelo abaixo e, a partir dele, componha sua apresentação pessoal. My name is Anne Eggsample. I am 38 years old. I am from the Windy City, Chicago. I am a pharmacist. I work at a local drugstore. I speak English and Spanish. I like reading, dancing and bungee jumping. My favorite music is heavy metal. I listen to Metallica and Skid Row driving to work. ETEC de Praia Grande Curso Técnico de Farmácia Inglês Instrumental Prof.ª Loren L. Damásio Nome: ...................................................................................... nº........... 3FR..... 7. Responda as perguntas a seguir: 21 a. Are you a pharmacist? ______________ b. Are you a man? ______________ c. Are you single? ______________ d. Are you American? ______________ e. Are you sick? ______________ f. Are you about 30 years old? ______________ g. Are you pregnant? ______________ h. Are you hypertensive? ______________ i. Are you allergic to penicillin? ______________ j. Is cancer contagious? ______________ 8. Complete o formulário abaixo com suas informações pessoais: Full Name: Birthdate: Marital Status: single ( Nationality: Address: Neighborhood: Email: Home number: Mobile number: ) married ( ) Sex: female ( divorced ( ) Occupation: City/State: Zipcode: ) male ( ) widow(er) ( ) 9. Continue fazendo o mesmo: a. What is your name? ______________________ b. What is your profession? ______________________ c. What is your marital status? ______________________ d. What is your nationality? ______________________ e. Where is your hometown? ______________________ f. When is your birth date? ______________________ g. How is your health condition lately? ______________________ h. How much is cocktail medication for AIDS patients? ______________________ i. Who is qualified to advice patients on the proper use of medications? _____________________ 10. Responda as perguntas, associando as letras aos números. 1. What do doctors do? 2. What does a pediatrician do? 3. What do ophthalmologists do? 4. What does a nutritionist do? a) They treat diseases related to the eyes. 5. What do physiotherapists do? b) They prepare medicines and dispense prescriptions. 6. What do pharmacists do? c) (S)He takes care of people’s teeth. 7. What does a dentist do? d) (S)He takes care of children and teen’s health. 8. What does a nurse do? e) They treat people who are ill or hurt and prescribe medicines. f) (S)He advises on matters of food and nutrition impacts on health. g) (S)He takes care for people who are ill or injured, especially in a hospital. h) They work with patients whose muscles are injured after accident or surgery. ETEC de Praia Grande Curso Técnico de Farmácia Inglês Instrumental Prof.ª Loren L. Damásio Nome: ...................................................................................... nº........... 3FR..... LESSON 5 1. Observe a capa da Newsweek e a manchete da reportagem principal. Em seguida, responda: qual o provável assunto da matéria? ETEC de Praia Grande Curso Técnico de Farmácia Inglês Instrumental Prof.ª Loren L. Damásio 22 Nome: ...................................................................................... nº........... 3FR..... 2. Com base em seu conhecimento prévio sobre o assunto e utilizando a estratégia skimming, faça uma primeira leitura do texto “A brief introduction to a new global epidemic” e verifique se as suas previsões estavam corretas. ETEC de Praia Grande Curso Técnico de Farmácia Inglês Instrumental Prof.ª Loren L. Damásio 23 Nome: ...................................................................................... nº........... 3FR..... 24 3. No texto, alguns dados são apresentados em porcentagem. Relacione-os ao tipo correspondente de representação gráfica: A B C D Principais causas de deficiência nos países desenvolvidos Taxas de depressão nos principais países Distúrbios mais frequentes Principais causas de incapacidade em nível mundial Mapas Gráfico em forma de pizza Tabela (Top causes of disability in developed countries) Tabela (Top causes of disability in all countries) Informação Não-Verbal Informação não-verbal é toda informação fornecida por meio de figuras, gráficos, tabelas, mapas etc. O leitor poderá se concentrar neles a fim de obter a informação que deseja ou necessita. No entanto, sabe-se que, não raro, a informação não-verbal é ignorada ou considerada supérflua pelo leitor. Contudo, se o autor a colocou à disposição, é porque ela deve ser observada. De fato, em muitos textos que combinam informação verbal e não-verbal, aquilo que se busca pode estar apenas num gráfico ou tabela, por exemplo. Nesse caso, a leitura do texto passa a ser apenas a confirmação das informações obtidas por meio de tais recursos. ETEC de Praia Grande Curso Técnico de Farmácia Inglês Instrumental Prof.ª Loren L. Damásio Nome: ...................................................................................... nº........... 3FR..... 4. Observando a informação não-verbal apresentada no texto, localize os seguintes dados: A – número total de pessoas que sofrem de algum tipo de distúrbio mental: B – principal causa de deficiência nos países desenvolvidos: C – posição que a depressão unipolar ocupa nos países desenvolvidos e em nível mundial: D – causas de deficiência constatada tanto nos países desenvolvidos quanto em nível mundial: E – porcentagem de casos de depressão no Brasil: F – países onde as taxas de depressão são as mesmas: 5. Localize as seguintes informações no texto: A – possíveis causas da depressão: B – sintomas mais comuns: C – tratamentos utilizados: D – tipos mais comuns de depressão e seu grau de incidência em homens, mulheres e crianças: 6. Preencha os excertos abaixo com as palavras dos quadros. Em seguida, atribua-lhes um título em português. ANTIDEPRESSANTS DOPAMINE CHEMICALS I. TÍTULO: ____________________________________ When certain _____________ in the brain (such as serotonin, norepinephrine, and _____________) are out of balance, depression occurs. Antidepressants improve the symptoms of depression by bringing these chemicals back into balance. Because different types of _____________ are designed to work differently, side effects associated with each type of depression medication vary. MEDICATION SYMPTOMS TREATMENT II. TÍTULO: ____________________________________ In order to decide on the best _____________ for depression, doctors must consider a variety of factors including _____________, any other medical conditions or medications taken, and any potential side effects that a new antidepressant causes. Specific side effects vary based on the type of depression _____________ that is prescribed. The most common side effects associated with antidepressants include: nausea, dry mouth, diarrhea or constipation, problems with sexual health, dizziness, problems sleeping, drowsiness, weight changes and anxiety/agitation. ETEC de Praia Grande Curso Técnico de Farmácia Inglês Instrumental Prof.ª Loren L. Damásio 25 Nome: ...................................................................................... nº........... 3FR..... LESSON 6 PART A FILL THE GAPS 1. Complete os espaços com verbos dados no presente simples, dados entre parêntesis PHARMACY TECHNICIAN DUTIES Being a pharmacy technician _____________ (be) a very important job. A pharmacy technician _____________ (answer) phone calls, _____________ (take) prescriptions from patients, and _____________ (distribute) the prescriptions to the patients for pick-up. The most important duty of a pharmacy technician _____________ (be) filling prescriptions. 2. Desembaralhe as partes de cada item, restaurando o sentido das frases. STEPS ON HOW TO FILL A PRESCRIPTION IN A PHARMACY 1. Enter / computer system. / prescription /into the 2. that is / Get label/ from the computer. / printed off 3. and take it back/ on the label / to the pharmacy counter./ pull drug from shelf,/ Look at drug name 4. of the drug/ on the label./ counting tray./ Count out the quantity/ that is listed/ Pour drug onto 5. into a vial / pour it / and place label around it./ Once the drug is counted, 6. to the pharmacist/ Give the drug stock bottle/ to be checked for correctness./ and vial that has been prepared/ 7. then be stored away,/ If the prescription is correct,/ or given to the patient./ then the prescription may be bagged,/ 3. Associe os números do exercício anterior às imagens abaixo: ( ) ETEC de Praia Grande Curso Técnico de Farmácia ( Inglês Instrumental Prof.ª Loren L. Damásio ) 26 Nome: ...................................................................................... nº........... 3FR..... 27 ( ( ) ) ( ) ( ) PART B 1. Após ver o vídeo, preencha os espaços em branco com as palavras omitidas, dadas no quadro. PHARMACY TECHNICIANS (video transcription) PROFESSION THANK YOU MEDICATION SIDE MEDICINE PATIENT DRUG WELL HEALTHY CLINICS DOCTOR When a prescription is written for a ___________ or a treatment, the next step for the ___________ is usually a visit to the pharmacist. “15 minutes ok? ___________.” And while for most people that often means going to the local drugstore, hospitals and community ___________ have pharmacies as well. Typically, pharmacists spend most of the day standing at a counter, dispensing ___________. They may also compound the medication, though this is now a much smaller part of a pharmacist’s practice. Well, many of the drugs they handle are pre-packaged by manufacturers, pharmacists are expected to understand the ingredients and how they might interact with other medications. This is a ___________ that requires careful attention to detail. Making a mistake and dispensing the wrong ___________ could have life-threatening consequences. “Ok, so your prescription is all set. What the ___________ wrote is a medication to help you sleep.” Part of the job is being able to explain to people how the prescription should be taken or administered, and providing information on drug interactions and ___________ effects. “Just be careful when you wake up in the morning. Sometimes you might feel a little hungover, a little drowsy.” ETEC de Praia Grande Curso Técnico de Farmácia Inglês Instrumental Prof.ª Loren L. Damásio Nome: ...................................................................................... nº........... 3FR..... There is also a lot of paper work involved. To study to become a pharmacist, you must first prove your aptitude in Science and Math, by passing the Pharmacy College Admission Test. After earning a Doctor of Pharmacy degree at College or University, pharmacists then need to be licensed by the State. With additional education, pharmacists can move into administration or teaching. They can even do research to develop new drugs. But the goal is the same; helping people get the medication they need to get ___________ and stay ___________. In: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EewBOBqrwNI&feature=related 2. Após a leitura do texto abaixo, faça o pedido nos itens de A a D: A. Ao que os termos em negrito, transcritos abaixo, dizem respeito? HOSPITAL: FACILITY: DEPARTMENT: SCHEDULE: SHIFT: HOURS: JOB DETAILS: B. Destaque no texto os verbos no tempo presente. C. O suporte mais provável para o texto seria um(a): ( ) prontuário medico ( ) cartaz de evento ( ) relatório D. Como o técnico de farmácia interessado deve proceder? ETEC de Praia Grande Curso Técnico de Farmácia Inglês Instrumental Prof.ª Loren L. Damásio ( ) jornal 28 Nome: ...................................................................................... nº........... 3FR..... 3. Ligue as informações do lado esquerdo da tabela às do lado direito. ( ) laboratory instruments ( ) measurement instruments ( ) types of medication 29 A) Capsules, injection, ointment, paste, powder, spray, syrup, tablets B) doctor or physician; pharmacist, chemist or druggist; pharmacy technician; patient C) counting tray, spatula, glass stirring rod, conical measuring flask, pestle and mortar ( ) personal D) Erlenmeyer flask, beaker, pipette, burette 4. Complete os quadros com as informações presentes nos itens A e B: CHART A headaches – treat anxiety – Opioids – Dextroamphetamine and Methylphenidate Prescription Drug Example CNS Depressants Barbiturates and Benzodiazepines CNS Stimulants Indication Side Drug Effects confusion and dizziness improve your attention Morphine, Codeine, Oxycodone, Hydrocodone relief pain drowsiness and constipation CHART B insomnia with pain – constipation – 1 or 2 tablets after meals and at bedtime – diabetic retinopathy – analgesic Prescription Drug Posology Indication swings in mood lack of appetite dryness of mouth 2 tablets at bedtime heartburn and acid indigestion antacid coagulant Side Effects nausea or gastric discomfort 2 to 3 tablets at meals 5. Escolha três medicamentos do exercício anterior e escreva frases com as informações das tabelas, usando as “fórmulas” abaixo, conforme o modelo. Providing information on drug interactions: What the doctor wrote was … Explaining how the prescription should be taken or administrated: Take … Providing information on side effects: Sometimes you might have/feel … ETEC de Praia Grande Curso Técnico de Farmácia Inglês Instrumental Prof.ª Loren L. Damásio Nome: ...................................................................................... nº........... 3FR..... MODELO 30 What the doctor wrote was a medication to help you sleep. Take 1 tablet by oral route every 8 hours for 10 days. Sometimes you might feel a little hungover, a little drowsy.” 1 2 3 LISTENING ACTIVITY TASK 1 Ouça o diálogo e complete os espaços em branco. Nurse: Good news, Wayne. The _____________ says you can go home now. Wayne: Great! Nurse: But before you leave, can I just _____________ on a few things? Wayne: Sure. Nurse: The doctor would like you to take these _____________. You have to take one pill every eight hours until they are all finished. There is enough for a week. OK? Wayne: OK. So one when I get up, one at lunchtime, and one before I go to bed. Nurse: Right. Now, Dr. Tan says you have a mild concussion and so you must not drive for at least a week. Wayne: No problem. I don’t really feel like driving at the moment. Nurse: OK, now your jaw. You mustn’t open your _____________ wide for a few days. Wayne: What if I have to yawn? Nurse: Good point. If you support your jaw with your _____________, it should help. Wayne: OK. TASK 2 Após ouvir o áudio, selecione dentre os itens abaixo aqueles que são mencionados. DISCHARGE INSTRUCTION GUIDELINE MAKE SURE PATIENT KNOWS: The name of the doctor who treated him/her. The diagnosis. Dose and possible side effects of medication or treatment. Precautions to be taken, e.g., no driving, complete rest for two weeks. What to do if the condition fails to improve or worsens. Date and time of follow-up (if any). ETEC de Praia Grande Curso Técnico de Farmácia Inglês Instrumental Prof.ª Loren L. Damásio Nome: ...................................................................................... nº........... 3FR..... LESSON 7 PART A TASK 1 Crossword Puzzle Across 1. We chew with these. 3. Where the legs bend. 5. We hear with these. 7. We walk on these. 8. Used for picking things up. 10. We smell with this. 11. The baby sucked his… Down 1. The upper part of the leg. 2. We taste with this. 4. We see with these. 6. This covers the body. 7. We kiss with these. 9. Attached to the shoulder. TASK 2 Encontre palavras relacionadas à doença, seguindo as instruções dos itens de 1 a 9. P H J H E A D A C H E P P A B Q S T O M A C H A C H E I Q A R L O I P J G Q E T Z O U W C V Z W R P L M N B V X U E E K A C A Z E A R A C H E R H T A P O Q A Z T W E F V B Q C Y C A U G L L I H S D J M A A U H A G W S S B P R D C C S H I E X H Q P W E H S O S A C T O R C U T P G D F L S A S C O P T V B T G D S D U N C T V O P U F E V E R R F Y H I K B T O A N D D S H I H S S F H K P A C 1. An ache or pain in the back, especially the lower back. 2. Pain in the ear; otalgia. 3. Pain in the head. 4. Pain in the stomach or abdominal region. 5. A pain in or about a tooth; odontalgia. 6. Common symptoms are sore throat, runny nose, nasal congestion, sneezing and cough. 7. Also known as tussis. It is a sudden, often repetitive, contraction of the thoracic cavity. 8. A frequent medical symptom that describes an increase in internal body temperature. 9. Any of various inflammations of the tonsils, characterized by pain in swallowing. ETEC de Praia Grande Curso Técnico de Farmácia Inglês Instrumental Prof.ª Loren L. Damásio 31 Nome: ...................................................................................... nº........... 3FR..... TASK 3 Ligue os números às figuras correspondentes. 1) CAPSULES 4) OITMENT 2) INHALER 5) PASTE 8) SUPPOSITORY 32 3) INJECTION 6) POWDER 7) SOLUTION 9) SYRUP 10) TABLETS PART B 1. Associe as vias de administração de remédios à afirmação correspondente. (A) Oral (B) Buccal/Sublingual (E) Subcutaneous (F) Inhalation (C) Rectal (G) Intramuscular (D) Intravenous (H) Topical ( ) 1 This process is also known as inspiration. Absorption of gases is relatively efficient, but not solids and liquids. ( ) 2 Most commonly by suppository or enema. ( ) 3 Local effect - eye drops, ear drops, antiseptic, callous removal, etc. ( ) 4 Many drugs are taken by mouth, as tablets, capsules, or drops. Some advantages are portability, lack of pain, facility to take. ( ) 5 Some drugs are taken as smaller tablets that are held in the mouth or under the tongue. ( ) 6 Drugs may be given into a peripheral vein over 1 to 2 minutes or longer by infusion. Rapid injections are used to treat epileptic seizures, acute asthma, or cardiac arrhythmias ( ) 7 This involves administration of the drug dose just under the skin. The drug can be given by patient, e.g. in the case of insulin, but it can cause pain. ( ) 8 The drug is taken via muscle, such as many vaccines, antibiotics. ETEC de Praia Grande Curso Técnico de Farmácia Inglês Instrumental Prof.ª Loren L. Damásio Nome: ...................................................................................... nº........... 3FR..... 2. Associe a Classificação Farmacológica à Indicação correspondente: 33 (A) Antitussives and Expectorants (B) Vitamins (C) Antiviral agent (D) Vasodilators, hypotensive medicines (E) Serum cholesterol reducers (F) Analgesic combinations (G) Ophthalmic preparation (H) Antibiotics (I) Anesthetics (J) Antiseptics (D) Antidiarrheal in combination with anti-infective agents ( ) 1 Provides rapid relief from irritations due to dust, allergies, swimming, smoke, smog, exposure to wind and cinema. ( ) 2 Treatment of specific and non-specific gastro-enteritis. ( ) 3 For the symptomatic relief of mild to moderate pain, and fever. ( ) 4 Treatment of initial and recurrent Herpes simplex infections of the skin and mucous membranes. ( ) 5 For the prevention of Vitamin C deficiency, as a vitamin supplement. ( ) 6 Treatment and prophylaxis of angina pectoris. ( ) 7 Indicated for use in the treatment of respiratory tract infection. ( ) 8 Indicated to decrease elevated serum total cholesterol and LDL cholesterol. ( ) 9 For the relief of coughs associated with respiratory infection, bronchospasm and allergy. ( ) 10 Induction of anesthesia. ( ) 11 Disinfection of the hands prior to surgery procedures or in the operating theater. ETEC de Praia Grande Curso Técnico de Farmácia Inglês Instrumental Prof.ª Loren L. Damásio Nome: ...................................................................................... nº........... 3FR..... LESSON 8 PART A TASK 1 Dê um título para o texto abaixo: _________________________ Today the cosmetic products range from simple skin creams, soaps and shampoos to special lotions, base creams, moisturizers, nourishers, cleansers, protectors, rejuvenators and conditioners for body, face, hands, eyes, lips, mouth, hair, nails and so on. TASK 2 Associe as palavras abaixo à sua definição e, em seguida, cace as palavras. (1) soap (2) perfume (3) cream (6) body lotion (4) fragrance (7) shampoo (5) lipstick (8) deodorant ( ) a substance that you put on your body to prevent or hide unpleasant smells. ( ) a liquid which people put on their bodies to make themselves smell pleasant. ( ) a soapy liquid used for washing hair. ( ) a substance used for washing the body which is usually hard, often has a pleasant smell, and produces a mass of bubbles when rubbed with water. ( ) a soft substance that you rub into your skin. ( ) a liquid with a pleasant smell, usually made from oils taken from flowers or spices, which is used on the skin. ( ) a liquid that you put on your skin in order to protect it, improve its condition or make it smell pleasant. ( ) a colored substance that women put on their lips to make them more attractive. ETEC de Praia Grande Curso Técnico de Farmácia Inglês Instrumental Prof.ª Loren L. Damásio 34 Nome: ...................................................................................... nº........... 3FR..... TASK 3 A tabela abaixo apresenta as propriedades de três importantes cosméticos. complete a tabela, especificando-os. 1. TOOTHPASTES REQUIRED PROPERTIES COSMETICS PRODUCTS 2. SHAMPOO ___________________ Protection against sunburns (immediate effects of sun exposure) Protection against long-term damages on cells However may allow few tan Water-resistant Pleasant feeling during and after application Easy spreadibility Easy-to-use Stable formulation Non-irritant, nonallergenic 3. SUN PROTECTION CREAM ___________________ ___________________ Consistence have to be creamy Thixotropic, enabling it to stand up on the toothbrush after it is extruded Easily washable Abrasive enough Pleasant taste Slightly foaming properties Homogeneous Well-tolerated by gingiva and buccal mucous Cleansing properties without eliminating all surface lipids Foaming properties Make hair shine and soft Make hair easy to comb Antistatic Pleasant odor Non-irritant, nonstinging TASK 4 Circule os adjetivos presentes no quadro da tarefa anterior. PART B 1. Após a leitura do texto, responda as perguntas. ( ) ingredientes para balanceamento de ácido e base ( ) ingredientes importantes do xampú ( ) principal ingrediente do xampú ( ) função do condicionador ( ) função do xampú ( ) uso do xampú ETEC de Praia Grande Curso Técnico de Farmácia 1 Shampoo is a common hair care product used for the removal of oils, dirt, skin particles, environmental pollutants and other contaminant particles that gradually build up in hair. 2 Shampooing is frequently followed by conditioners which 3 increase the ease of combing and styling. 4 Shampoo is generally made by combining a detergent in water to form a thick, viscous liquid. 5 Other essential ingredients include salt (sodium chloride), a preservative and fragrance. 6 Acids or bases such as citric acid or sodium hydroxide are added to adjust the pH of a shampoo so the detergents will provide optimal cleaning. Inglês Instrumental Prof.ª Loren L. Damásio 35 Nome: ...................................................................................... nº........... 3FR..... 2. Complete os espaços em branco do texto PH SCALE com as palavras do quadro abaixo. vinegar basic water neutral milk acids Acidic and _____________ are two extremes that describe a chemical property. Mixing _____________ and bases can cancel out or neutralize their extreme effects. A substance that is neither acidic nor basic is _____________. The pH scale measures how acidic or basic a substance is. The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14. A pH of 7 is neutral. A pH less than 7 is acidic. A pH greater than 7 is basic. Pure _____________ is neutral. But when chemicals are mixed with water, the mixture can become either acidic or basic. Examples of acidic substances are _____________ and lemon juice. Detergent, _____________ of magnesia, and ammonia are examples of basic substances. PART C PREVENTING ILLNESS Rather than treat an illness, patients should prevent disease in the first place. Depending on one's beliefs about the body and the causes of disease, such prevention (or ‘prophylaxis’) can take many forms. It may include diets and exercise, vaccination and drugs. Disease Prevention Through Nutrition The health benefits and risks of foods has been and will always be a source of excitement, controversy, and research. Although it could seem that dietary recommendations change frequently, the consistent findings are that getting adequate sources of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants through foods are the best way to stay healthy. MODAL VERBS Os verbos modais são verbos distintos dos outros, pois possuem características próprias: 1. Não mudam de forma; 2. Não precisam de auxiliares; 3. Após os modais, o verbo principal deve vir no infinitivo, sem TO. São verbos modais: can (pode), could (poderia), may (pode, poderia), might (pode, poderia), should (deveria), must (deve), would (-ria) e will (-rá). ETEC de Praia Grande Curso Técnico de Farmácia Inglês Instrumental Prof.ª Loren L. Damásio 36 Nome: ...................................................................................... nº........... 3FR..... 37 TASK 1 Advices on health… Escolha a alternativa mais apropriada. 1. You _________ drink at least a gallon of water per day. a. can b. will c. should 2. Strawberries _________ make your teeth whiter. a. should b. could c. can 3. The doctor told me: “You _________ eat less sugar. a. must b. would c. may 4. If you continue eating so much fatty food, you _________ have cardiovascular problems. a. might b. could c. must 5. _________ I eat as many fruit and vegetables as I want? a. will b. can c. must 6. Your child is too fat. He _________ eat fewer sweets. a. would b. must c. should 7. To be in good health, you _________ walk at least half an hour. a. can b. may c. should 8. You _________ suffer from heart diseases because you eat too much junk food. a. must b. can c. might 9. 150kg!? You _________ lose weight. a. must b. will c. can 10. You _________ use less salt when you cook. It's bad for your health. a. would b. will c. can 11. You _________ eat more fruit and vegetables to be in good health. a. may b. should c. will Palavras-Chave Os termos mais recorrentes em um texto geralmente representam as palavraschave. Elas indicam o assunto do texto e são relevantes porque é em torno delas que o texto é construído. A palavrachave com mais força é a que pode figurar no título do texto. . ETEC de Praia Grande Curso Técnico de Farmácia Inglês Instrumental Prof.ª Loren L. Damásio Nome: ...................................................................................... nº........... 3FR..... THE FOOD CHEMICALS CODEX The Food Chemicals Codex (FCC) or Codex Alimentarius (Latin for "food code" or "food book") is a compendium of internationally recognized standards for purity and identity of food ingredients. The FCC was created in 1963 by Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and World Health Organization (WHO). The main purposes of this program are protecting health of the consumers and ensuring fair trade practices in the food trade, and promoting coordination of all food standards work undertaken by international governmental and non-governmental organizations. GLOSSÁRIO: Ensure: assegurar Standard: padrão Trade: comércio Undertake: empreender TASK 2 Após a leitura do texto, responda: a) Qual a palavra repetida no texto e qual seu significado em português? b) Quando foi criado o Codex Alimentarius? c) Quem criou o Codex Alimentarius? TASK 3 Em textos em inglês, nomes de instituições norte-americanas e órgãos internacionais são comuns quando o assunto é medicamentos. Associe as duas colunas abaixo conforme melhor convenha. 1) Federal Trade Commission (FTD) 2) United States of America (USA) 3) United Nations Organization (UNO) 4) Food and Drug Administration (FDA) 5) Food Chemicals Codex (FCC) 6) World Health Organization (WHO) 7) Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) ( ( ( ( ( ( ( ) Organização das Nações Unidas para a Agricultura e a Alimentação (FAO) ) Estados Unidos da América (EUA) ) Procuradoria de Proteção e Defesa do Consumidor (PROCON) ) Código Alimentar ) Organização Mundial da Saúde (OMS) ) Organização das Nações Unidas (ONU) ) Agência Nacional de Vigilância Sanitária (ANVISA) TASK 4 Speaking of food... Preencha os parêntesis dos itens abaixo com a letra correspondente dada na pirâmide alimentar ao lado. ( ( ( ( ) 1 Rice, beans, pasta, potatoes, grains ) 2 Fruits / Vegetables ) 3 Fats, oils, sugar, salt ) 4 Meat, dairy products, eggs ETEC de Praia Grande Curso Técnico de Farmácia Inglês Instrumental Prof.ª Loren L. Damásio 38 Nome: ...................................................................................... nº........... 3FR..... TASK 5 Relacione as fontes de vitamina e sua importância ao tipo de vitamina correspondente. VITAMINS vitamin C (ascorbic acid) vitamin E (tocopherol) vitamin B2 (riboflavin) vitamin A (retinol) vitamin B1 (thiamine) 1 _____________ : butter, egg yolk, milk and fish oils: important for normal growth, healthy skin, and the ability to see well, especially at night. 2 _____________ : grains, rice, nuts and liver: important for the production of energy from sugar and starch in the body and helping the heart, muscles and nervous system to work well. 3 _____________ : liver, milk, cheese, yeast and whole grains: important for the production of energy in the cells and for the production of particular hormones. 4 _____________ : citrus fruit, green vegetables, tomatoes and potatoes: important for healthy bones, joints, teeth and gums, and for fighting infection. 5 _____________ : vegetable oils, grains, green vegetables and fish: important for healthy blood and cells. TASK 6 Abaixo estão relacionados, em duas colunas, de uma lado, nomes de minerais e, de outro, sua(s) fonte(s). Associe as informações. 1 Potassium (K) 4 Calcium (Ca) ( ( ( ( ( ( 2 Chloride (Cl) 3 Sodium (Na) 5 Magnesium (Mg) 6 Iron (Fe) ) dairy products, canned fish with bones, green leafy vegetables, nuts and seeds ) red meat, leafy green vegetables, fish, eggs, dried fruits, beans, whole and enriched grains ) legumes, potato skin, tomatoes, and bananas ) nuts, soy beans, and cocoa mass ) table salt ) sea vegetables, milk, and spinach ETEC de Praia Grande Curso Técnico de Farmácia Inglês Instrumental Prof.ª Loren L. Damásio 39 Nome: ...................................................................................... nº........... 3FR..... LESSON 9 PART A 125th Anniversary On May 8, 1886, a pharmacist named Dr. John Pemberton carried a jug of Coca-Cola® syrup to Jacobs’ Pharmacy in downtown Atlanta, where it was mixed with carbonated water and sold for five cents a glass. From humble beginnings 125 years ago, Coca Cola® has grown from selling a modest 9 drinks a day in 1886 to 1.7 billion a day. And expanded from one city in one country to availability in more than 200 countries around the world. TASK 1 Procure no dicionário o significado das seguintes preposições: ABOUT - IN - TO - FOR - OF - WITH - FROM - ON - WITHOUT - TASK 2 Complete o quadro a seguir com informações extraídas do texto. TIMETABLE 125 years ago YEAR 1886 currently 1.7 billion a day SELLINGS PLACE Atlanta, GA, United States $1.50 a coke can or fountain PRICE TASK 3 Complete os espaços em branco dos números com a letra apropriada. 1 __NE 2 T__O 3 T__REE 4 FO__R 5 FIV__ 6 S__X 7 SEV__N 8 EIG__T 9 NIN__ 10 TE__ 11 ELEV__N 12 TWE__VE 13 TH__RTEEN 14 F__URTEEN 15 FI__TEEN 16 S__XTEEN 17 SEV__NTEEN 18 EI__HTEEN 19 NIN__TEEN 20 TWENT__ 21 TWENTY-__NE 22 TWENTY-T__O 23 TWENTY-T__REE 24 TWENTY-FO__R 25 TWENTY-FIV__ 26 TWENTY-S__X 27 TWENTY-SEV__N 28 TWENTY-EIG__T 29 TWENTY-NIN__ 30 T__IRTY 40 F__RTY 50 FI__TY 60 SIXT__ 70 SEVENT__ 80 EI__HTY 90 NIN__TY 100 ONE HUNDRED 101 ONE HUNDRED (AND) ONE 1,000 ONE THOUSAND 1,111 ONE THOUSAND (AND) ONE HUNDRED (AND) ELEVEN 10,000 TEN THOUSAND 10,562 TEN THOUSAND (AND) FIVE HUNDRED (AND) SIXTY-TWO 100,000 ONE HUNDRED THOUSAND 1,000,000 ONE MILLION 1,000,000,000 ONE BILLION ETEC de Praia Grande Curso Técnico de Farmácia Inglês Instrumental Prof.ª Loren L. Damásio 40 Nome: ...................................................................................... nº........... 3FR..... TASK 4 Escreva em inglês, por extenso, os números a seguir. 8 1886 125 9 1.7 billion 200 In MATH we use numbers, in CHEMISTRY we use quantities. A quantity is described by a number and a unit. 100 is a number; 100 Kg is a quantity. Que medidas você conhece para... distance? volume? mass (weight)? time? temperature? TASK 5 Metric Unit Conversion Problems: A) How many centimeters in 2 meters? B) How many grams in 150 pounds given the equalities 1 pound = 0.454 kg and 1 kg = 1000 grams? TASK 6 Abaixo estão as propriedades físicas de um comprimido de fenolftaleína. Associe as informações no quadro às propriedades descritas. <1 min 280 N biconvex 385 mg Tablet properties Weight ..........................................____________ Diameter .......................................9 mm Form..............................................____________ Hardness.......................................____________ Disintegration (water) ...................____________ Friability..........................................0.2% ETEC de Praia Grande Curso Técnico de Farmácia Inglês Instrumental Prof.ª Loren L. Damásio 41 Nome: ...................................................................................... nº........... 3FR..... 42 PART B SIMPLE PAST Dr. John Pemberton invented Coca Cola on 8 May 1886. Agatha Christie worked as a volunteer nurse and a pharmacy technician. Brittany Murphy took hundreds of pills the month she died. She was only 32 years old. No passado dos verbos regulares em inglês basta adicionar a terminação -ED. Atentando para os seguintes caso: Verbos terminados em -E é acrescido apenas de -D. Verbos terminados em Y antecedido por consoante, troca-se o Y por I. Cada verbo irregular, no entanto, possui uma forma própria que precisa ser memorizada. Todo dicionário traz uma lista desses verbos. 1. Complete o texto, dando o passado dos verbos em parêntesis. FIVE NOTABLE PHAMACISTS IN HISTORY A In the late 1700s, the founder of homoeopathy, Samuel Hahnemann, a physician, chemist, and linguist in Germany, _____________ (to propose) a new approach to treating illness. The first major step reportedly _____________ (to be) when he _____________ (to be) translating an herbal text and _____________ (to read) about a treatment cinchona bark) used to cure malaria. He _____________ (to take) some cinchona bark and _____________ (to observe) that, as a healthy person, he _____________ (to develop) symptoms that _____________ (to be) very similar to malaria symptoms. This _____________ (to lead) Hahnemann to consider that a substance may create symptoms that it can also relieve. This concept is called the "similia principle" or "like cures like." B Paracelsus (1493–1541) _____________ (to be) a Swiss Renaissance physician and alchemist who _____________ (to make) groundbreaking advances in the field of medicine. He _____________ (to pioneer) the use of chemicals and minerals in medicine. Paracelsus, sometimes called the father of toxicology, _____________ (to write): "The dose makes the poison." ETEC de Praia Grande Curso Técnico de Farmácia Inglês Instrumental Prof.ª Loren L. Damásio Nome: ...................................................................................... nº........... 3FR..... 43 C Believe it or not, the Founding Father, Benjamin Franklin, _____________ (to be) a pharmacist before he _____________ (to be) ever a printer, statesman, or infamous ladies man. Working as a clerk in a neighborhood mercantile store, he _____________ (to dispense) medicines, herbs and various curatives. The man who famously _____________ (to say), “An apple a day keeps the doctor away” apparently _____________knew (to know) what he _____________ (to be) talking about. D The renowned Norwegian playwright, Henrik Ibsen, _____________ (to spend) his teenage years working as a pharmacists apprentice. He _____________ (to leave) home at 15 and _____________ (to make) his way to the coastal town of Grimstad where he _____________ (to live) for six years, eventually becoming assistant pharmacist. Ibsen _____________ (to study) to become a physician but _____________ (to be) not a very good student – fortunately for theater lovers. E Sir Isaac Newton, the man who _____________ (to change) the world with his theory of gravity, _____________ (to serve) as an apprentice apothecary in Grantham, England, living with the town’s apothecary and becoming engaged to the boss’s daughter. He _____________ (to leave) both, however, to study at Cambridge, where he _____________ (to begin) his illustrious career in physics and mathematics. Newton never _____________ (to go) back to the pharmaceutical arts and he apparently _____________ (to give up) women, too – the apothecary’s daughter _____________ (to marry) someone else and Newton _____________ (to live) the rest of his life as a bachelor. 2. Complete o esquema a seguir com as palavras: FREEZING, GAS, LIQUID, SOLID, VAPORIZATION ETEC de Praia Grande Curso Técnico de Farmácia Inglês Instrumental Prof.ª Loren L. Damásio